Wifi Modes of an Access point: DLink has painted a nice overview over the possible different modes of an Accesspoint:
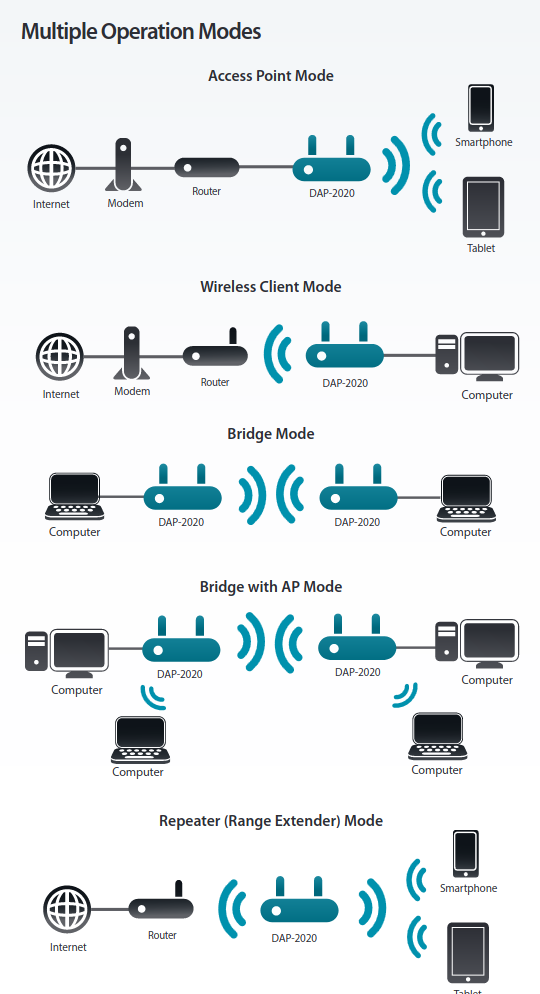
Multiple Operation Modes – Wireless Client Mode – Bridge Mode – Bridge with AP Mode – Repeater (Range Extender) Mode https://www.dlink.com/xk/sq/-/media/business_products/dap/dap-2020/datasheet/dap_2020_datasheet_uk_en.pdf
cybersec:
from great wifi modes that allow bridging two wifi networks, it would be GREAT if vendors test their products for possible security problems and provide updates at least 10 years after release
one-liner:
su - root ip -c a; # what is wifi nic name service NetworkManager stop iwconfig wlp3s0 essid 'HotelWifiWithNoPassword' iwconfig wlp3s0 essid 'HotelWifi' key 'password' dhclient wlp3s0
if wifi has no password set wpa_passphrase will complain and thus can not be used
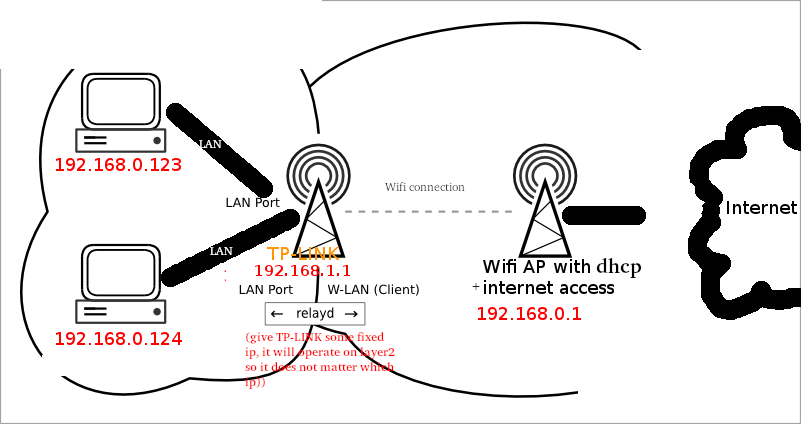
is it possible, to PC <-LAN-> AP <-Wifi-> AP <-> internet?
With those TP-LINK routers, Yes it is!
Why do other routers not have this “Wifi Bridge” (!) functionality?
It is rather simple:
the TPLink unfortunatel neither provides firmware updates nor was it very reliable, it worked for several years… then it started to make problems.
update: 2021-02
Fritzboxes have upgraded WLAN security to WPA2+WPA3… it seams the WDS was disabled?
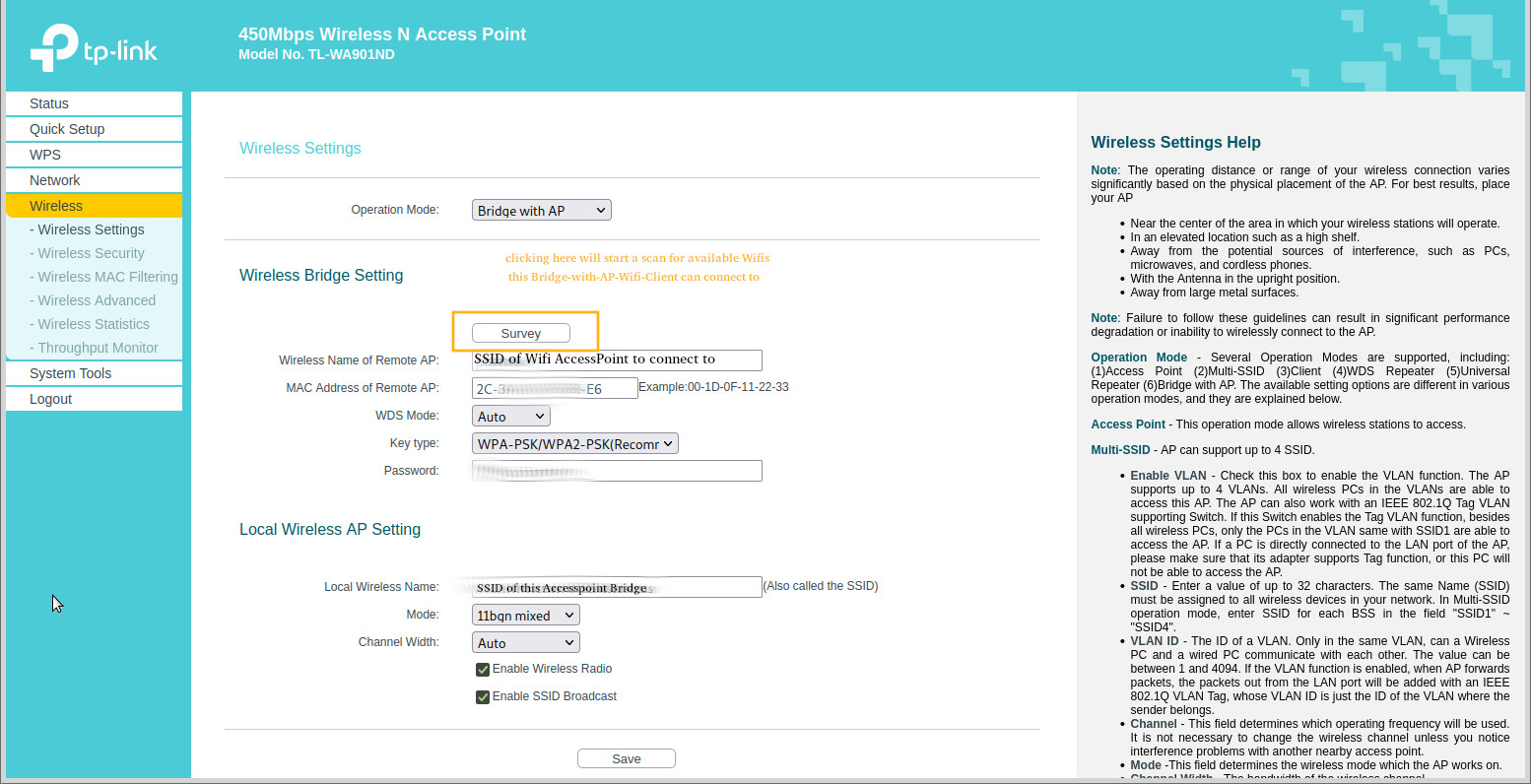
it is pretty nice what modes the TP-LINK WIFI Routers support, for example the TL-WA901ND v5 450Mbps Wireless N Access Point, it comes with PoE per default and offers those WIFI / WLAN modes:
the client mode can be especially interesting, the user can user the router like a LAN connected WIFI Dongle! 🙂
which is used on a daily basis with an older version: TP-Link TL-WR841N/ND v11
had no USB WIFI Dongle available so the question was: Why not use a spare Wifi-router as an AdHoc Wifi-Client to connect to the Wifi-internet instead of an USB dongle?
and it not only does that, but it also allows WIFI clients to connect to the Bridge and forwards the traffic to the central-internet-connected Wifi-AccessPoint (CICWAP).
Disable DHCP on the TP-LINK as the DHCP of the central-internet-connected Wifi-AccessPoint (CICWAP) will be used 😀
OpenWRT and has the WDS feature too, with TP-LINK no not even need to modify the firmware.
it is maybe not a perfect solution (dd-wrt or OpenWRT + relayd might be the cleaner solution)
Hardware used:
TP-LINK WR841N v11 00000000 in “bridge-with-ap-mode” connecting to Fritzbox 7490 Wifi (works pretty well)
what does not work so well is: TL-WA901ND <-bridge-with-ap-mode-> TL-WA901ND, get frequent disconnects/reconnects (every ~20min for 30sec?)
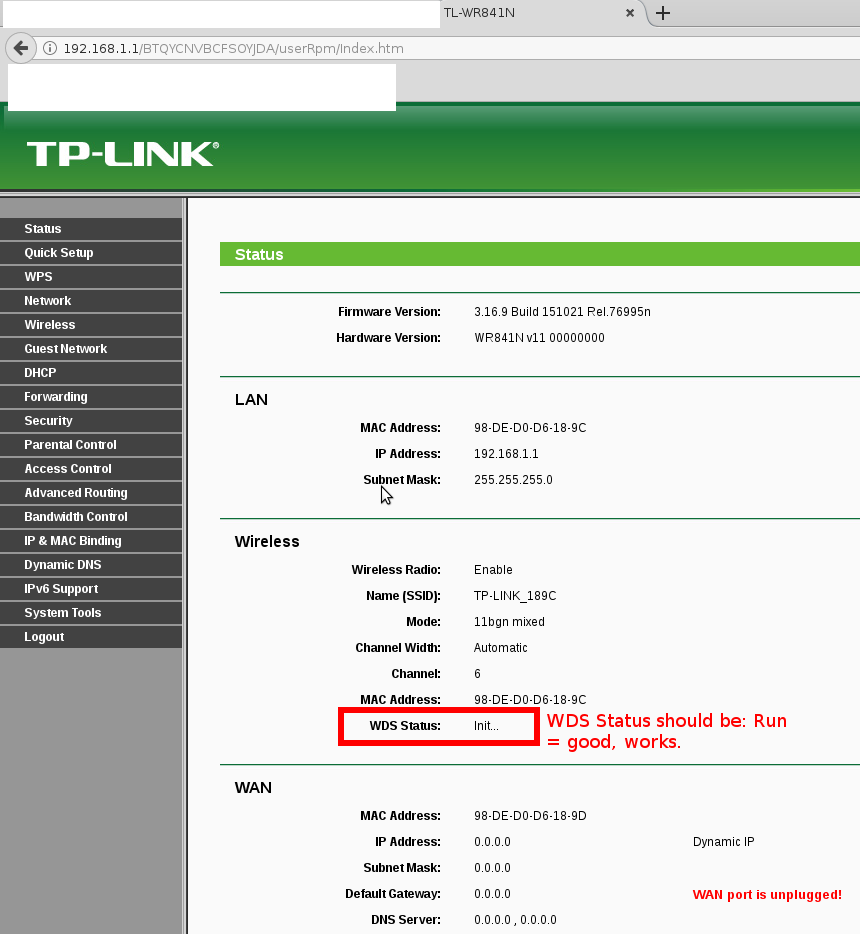
Firmware Version 3.16.9 Build 151021 Rel.76995n
config the router:
i assume you have factory defaults… when you connect via LAN cable to Port1 of your router – the router the first time you get an dynamic IP address 192.168.XXX.100.
So your router will be available at 192.168.XXX.1 – browse to that.
Default Username and Password are:
usr: admin
pwd: admin
- Disable WPS, UPnP – it is a security problem – maybe also IPv6 support if you do not need it (usually not inside LANs).
- You can leave the Firewall on.
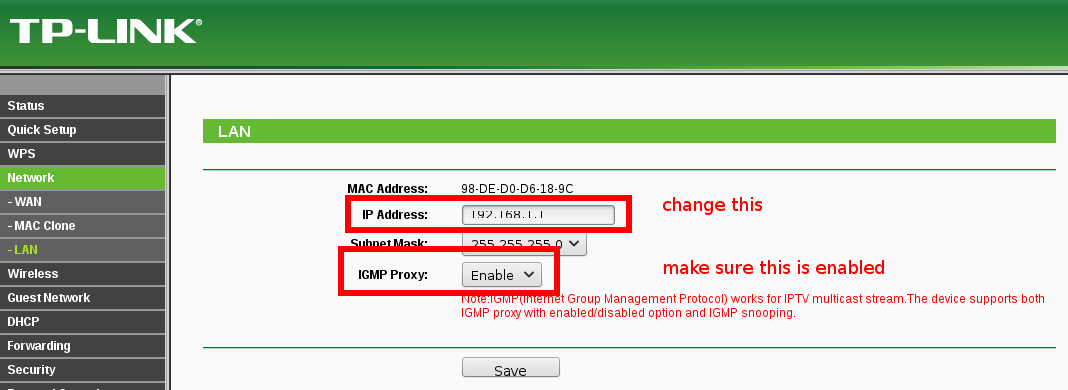
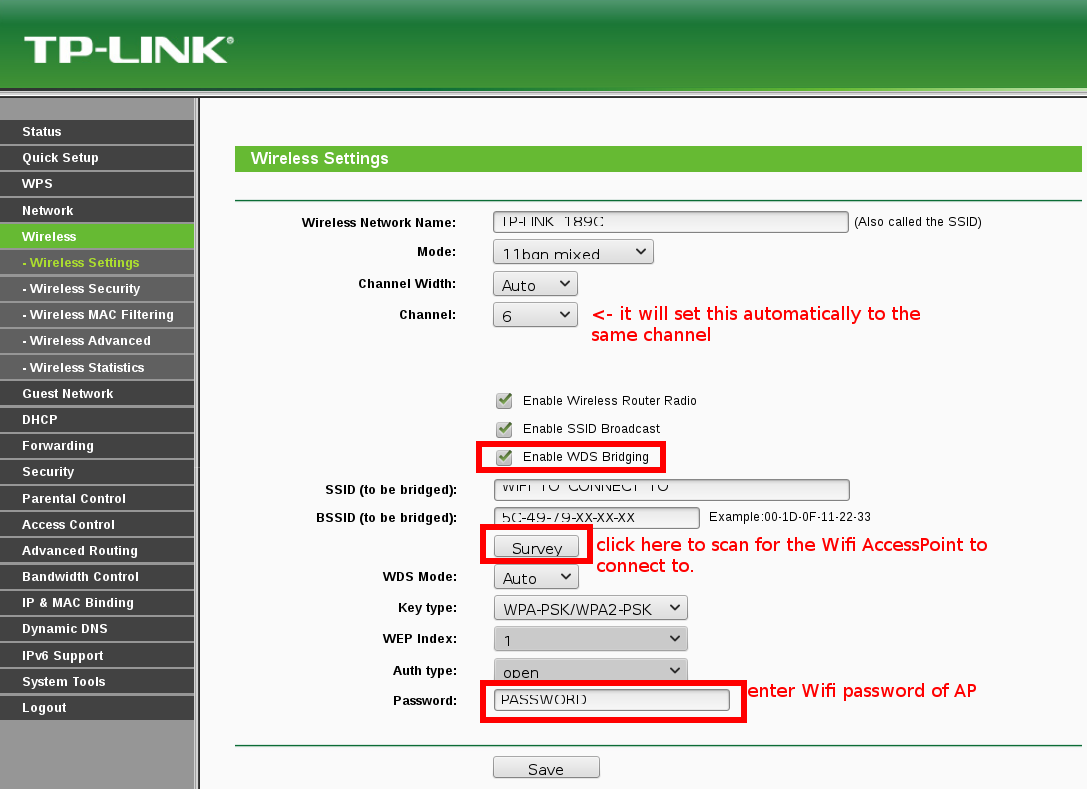
- Go to network settings: and change the router’s IP to something (e.g. 192.168.1.1) else than your Wifi AP’s network (192.168.0.1)
reboot the router and reconnect to the new IP…
save the settings… go to Wireless Security and give your TP-LINK a Wifi password.
then restart the router.
disable DHCP inside the TP-LINK router:
now your client’s should automatically get DHCP-assigned-IP-address from your main-internet enabled WiFi-Router.
if you need to reconnect with your router fire up a root terminal:
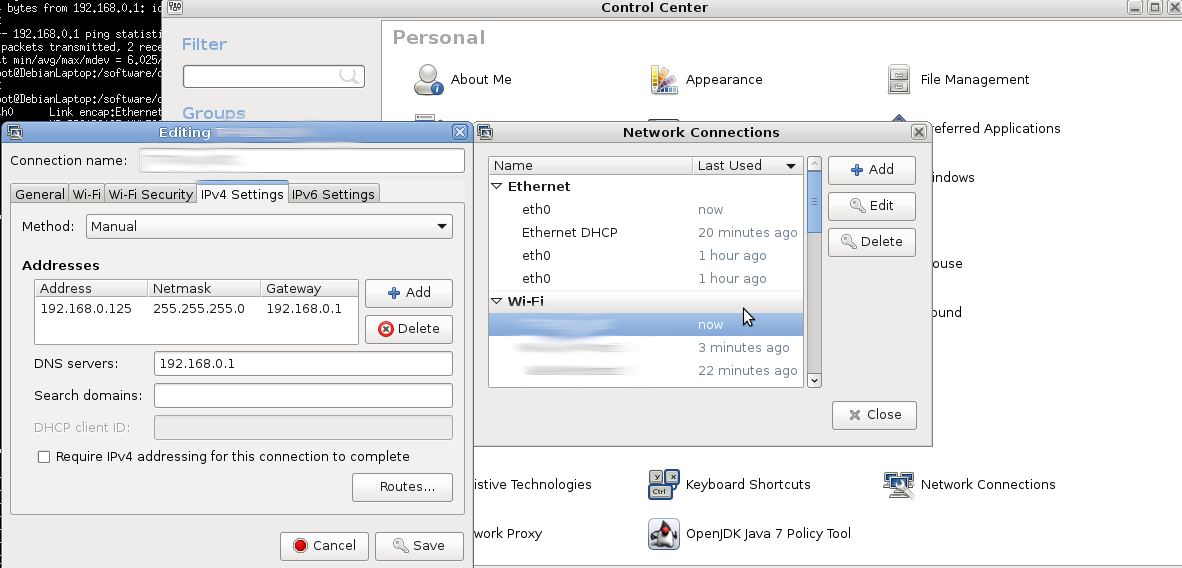
ifconfig eno1:0 192.168.1.123 up
and
ping 192.168.1.1
should work.
the router should now be able to connect to the internet via your other Wifi router.
if not try this:
optional: config the client(s)
but once this is configured – it works flawlessly.
the big antennas of the router provide pretty good reception.
ifconfig; # old command - not available in CentOS7 anymore :( eth5 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 00:e0:6f:28:fe:97 inet addr:192.168.0.127 Bcast:192.168.0.255 Mask:255.255.255.0 inet6 addr: fe80::2e0:6fff:fe28:fe97/64 Scope:Link ip addr show; # alternative command 2: eth5: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast state UP group default qlen 1000 link/ether 00:e0:6f:28:fe:97 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff inet 192.168.0.127/24 brd 192.168.0.255 scope global eth5 valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever inet6 fe80::2e0:6fff:fe28:fe97/64 scope link valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever ifconfig eth5:0 192.168.1.123 up; # give your NIC a new IP to access the router as well as internet at the same time ip route show; # show routes default via 192.168.0.1 dev eth5 proto static metric 1024 192.168.0.0/24 dev eth5 proto kernel scope link src 192.168.0.127 192.168.1.0/24 dev eth5 proto kernel scope link src 192.168.1.123 # you should be able to ping ping 192.168.1.1; # the tplink router PING 192.168.1.1 (192.168.1.1) 56(84) bytes of data. 64 bytes from 192.168.1.1: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.279 ms 64 bytes from 192.168.1.1: icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=0.277 ms 64 bytes from 192.168.1.1: icmp_seq=3 ttl=64 time=0.252 ms ^C ping 192.168.0.1; # the router that got internet PING 192.168.0.1 (192.168.0.1) 56(84) bytes of data. 64 bytes from 192.168.0.1: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=4.52 ms 64 bytes from 192.168.0.1: icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=4.64 ms 64 bytes from 192.168.0.1: icmp_seq=3 ttl=64 time=3.01 ms ping yahoo.de; # the internet PING yahoo.de (98.137.236.24) 56(84) bytes of data. 64 bytes from aviate.yahoo.com (98.137.236.24): icmp_seq=1 ttl=46 time=193 ms 64 bytes from aviate.yahoo.com (98.137.236.24): icmp_seq=2 ttl=46 time=195 ms 64 bytes from aviate.yahoo.com (98.137.236.24): icmp_seq=3 ttl=46 time=204 ms
VOILA!
btw the probably (only?) stick that works out of the box an 99% of all GNU Linux?
liked this article?
- only together we can create a truly free world
- plz support dwaves to keep it up & running!
- (yes the info on the internet is (mostly) free but beer is still not free (still have to work on that))
- really really hate advertisement
- contribute: whenever a solution was found, blog about it for others to find!
- talk about, recommend & link to this blog and articles
- thanks to all who contribute!