on the one hand – software biodiversity is good – if one system get’s hacked or virus infiltrated – the other’s – if “different enough” probably stay unaffected.
on the other hand – if config files or procedures or command line tools are not standardized accross distributions = makes things too complicated = hard to comprehend and remember = causes errors and wastes time = bad 😀
*.deb GUN Linux (Debian, Ubuntu, Mint)
root@Debian9:~# which ifup /sbin/ifup root@Debian9:~# file /sbin/ifup /sbin/ifup: ELF 32-bit LSB executable, Intel 80386, version 1 (SYSV), dynamically linked, interpreter /lib/ld-linux.so.2, for GNU/Linux 2.6.32, BuildID[sha1]=33b7cd4bf09f8be12422d3c2a7aceb157341fef2, stripped FILES /etc/network/interfaces definitions of network interfaces See interfaces(5) for more information.
example content:
root@Debian9:~# cat /etc/network/interfaces # This file describes the network interfaces available on your system # and how to activate them. For more information, see interfaces(5). source /etc/network/interfaces.d/* # The loopback network interface auto lo iface lo inet loopback # The primary network interface allow-hotplug eth0 iface eth0 inet dhcp
/run/network/ifstate
current state of network interfaces
the above example content displays eth0 using DHCP.
luckily things don’t change with every new version, if you would like to have a fixed ip change it to something like:
# This file describes the network interfaces available on your system
# and how to activate them. For more information, see interfaces(5).
# The loopback network interface
auto lo
iface lo inet loopback
# The primary network interface
# allow-hotplug eth0
# iface eth0 inet dhcp
# fixed ipc
auto eth0
iface eth0 inet static
address 192.168.1.222
netmask 255.255.255.0
gateway 192.168.1.1
ESC :X # save and quit in vim
root@Debian8:~# service networking restart
and settings should be active.
*.rpm (Redora/CentOS/Redhatz) gui mode:
Type this command to see network interfaces on this server.
# install nmcli and nmtui yum update yum install NetworkManager NetworkManager-tui systemctl enable NetworkManager systemctl start NetworkManager # hopefully shows active and running # reboot if not systemctl status NetworkManager # list all network devices nmcli d DEVICE TYPE STATE CONNECTION br-14e91f91a6bc bridge connected br-14e91f91a6bc docker0 bridge connected docker0 eth0 ethernet connected eth0 lo loopback unmanaged --
And type this command to open Network Manager.
nmtui
which restults into this config:
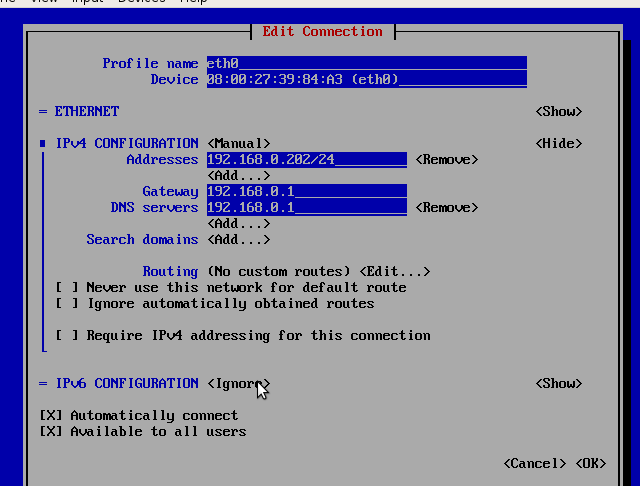
vim /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0 HWADDR=08:00:27:39:84:A3 TYPE=Ethernet PROXY_METHOD=none BROWSER_ONLY=no BOOTPROTO=none IPADDR=192.168.0.202 PREFIX=24 GATEWAY=192.168.0.1 DNS1=192.168.0.1 DEFROUTE=yes IPV4_FAILURE_FATAL=no IPV6INIT=no NAME=eth0 UUID=469f7b2f-88d0-3ab4-8d7a-88d0db0ac469 ONBOOT=yes AUTOCONNECT_PRIORITY=-999
terminal mode: activate network on boot
you can do it the manual way (see below) or use:
nmtui; # the all you need cool network config tool
*.rpm (Redora/CentOS/Redhatz) manual way:
search how to set fixed ip on centos7
which ifup /usr/sbin/ifup file /usr/sbin/ifup /usr/sbin/ifup: Bourne-Again shell script, ASCII text executable
vim /etc/sysconfig/network
example content:
[root@CentOS7 ~]# cat /etc/sysconfig/network # Created by anaconda NETWORKING=yes [root@CentOS7 ~]# cat /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0 TYPE=Ethernet BOOTPROTO=dhcp DEFROUTE=yes PEERDNS=yes PEERROUTES=yes IPV4_FAILURE_FATAL=no IPV6INIT=no <- if it is a server or router "yes" IPV6_AUTOCONF=no <- if it is a server or router "yes" IPV6_DEFROUTE=no <- if it is a server or router "yes" IPV6_PEERDNS=no <- if it is a server or router "yes" IPV6_PEERROUTES=no <- if server or client "no" IPV6_FAILURE_FATAL=no IPV6_ADDR_GEN_MODE=stable-privacy NAME=eth0 UUID=1f926ad0-9cd9-4adb-b8ec-5993ae40e333 DEVICE=eth0 ONBOOT=yes <- change this, it is no per default, which means no auto startup of network, then reboot system.
/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-<configuration>
The file defining an interface.
after all that restart network to make changes active
service network restart
GNU Linux Suse12
search how to set fixed ip on suse12
suse12:~ # which ifup /sbin/ifup suse12:~ # file /sbin/ifup /sbin/ifup: symbolic link to `/usr/sbin/ifup' suse12:~ # file /usr/sbin/ifup /usr/sbin/ifup: Bourne-Again shell script, ASCII text executable FILES /sbin/ifup The script itself. vim /etc/sysconfig/network/config # General configuration options.
example content:
suse12:~ # cat /etc/sysconfig/network/ifcfg-eth0 BOOTPROTO='dhcp' BROADCAST='' ETHTOOL_OPTIONS='' IPADDR='' MTU='' NAME='' NETMASK='' NETWORK='' REMOTE_IPADDR='' STARTMODE='auto' DHCLIENT_SET_DEFAULT_ROUTE='yes' suse12:~ # cat /etc/sysconfig/network/config ## Path: Network/General ## Description: Global network configuration # # Note: # Most of the options can and should be overridden by per-interface # settings in the ifcfg-* files. # # Note: The ISC dhclient started by the NetworkManager is not using any # of these options -- NetworkManager is not using any sysconfig settings. # ## Type: yesno ## Default: yes # If ifup should check if an IPv4 address is already in use, set this to yes. # # Make sure that packet sockets (CONFIG_PACKET) are supported in the kernel, # since this feature uses arp, which depends on that. # Also be aware that this takes one second per interface; consider that when # setting up a lot of interfaces. CHECK_DUPLICATE_IP="yes" ## Type: list(auto,yes,no) ## Default: auto # If ifup should send a gratuitous ARP to inform the receivers about its # IPv4 addresses. Default is to send gratuitous ARP, when duplicate IPv4 # address check is enabled and the check were sucessful. # # Make sure that packet sockets (CONFIG_PACKET) are supported in the kernel, # since this feature uses arp, which depends on that. SEND_GRATUITOUS_ARP="auto" ## Type: yesno ## Default: no # Switch on/off debug messages for all network configuration stuff. If set to no # most scripts can enable it locally with "-o debug". DEBUG="no" ## Type: integer ## Default: 30 # # Some interfaces need some time to come up or come asynchronously via hotplug. # WAIT_FOR_INTERFACES is a global wait for all mandatory interfaces in # seconds. If empty no wait occurs. # WAIT_FOR_INTERFACES="30" ## Type: yesno ## Default: yes # # With this variable you can determine if the SuSEfirewall when enabled # should get started when network interfaces are started. FIREWALL="yes" ## Type: int ## Default: 30 # # When using NetworkManager you may define a timeout to wait for NetworkManager # to connect in NetworkManager-wait-online.service. Other network services # may require the system to have a valid network setup in order to succeed. # # This variable has no effect if NetworkManager is disabled. # NM_ONLINE_TIMEOUT="30" ## Type: string ## Default: "dns-resolver dns-bind ntp-runtime nis" # # This variable defines the start order of netconfig modules installed # in the /etc/netconfig.d/ directory. # # To disable the execution of a module, don't remove it from the list # but prepend it with a minus sign, "-ntp-runtime". # NETCONFIG_MODULES_ORDER="dns-resolver dns-bind dns-dnsmasq nis ntp-runtime" ## Type: yesno ## Default: no # # Enable netconfig verbose reporting. # NETCONFIG_VERBOSE="no" ## Type: yesno ## Default: no # # This variable enables netconfig to always force a replace of modified # files and automatically enables the -f | --force-replace parameter. # # The purpose is to use it as workaround, when some other tool trashes # the files, e.g. /etc/resolv.conf and you observe messages like this # in your logs on in "netconfig update" output: # ATTENTION: You have modified /etc/resolv.conf. Leaving it untouched. # # Please do not forget to also report a bug as we have a system policy # to use netconfig. # NETCONFIG_FORCE_REPLACE="no" ## Type: string ## Default: "auto" # # Defines the DNS merge policy as documented in netconfig(8) manual page. # Set to "" to disable DNS configuration. # NETCONFIG_DNS_POLICY="auto" ## Type: string(resolver,bind,dnsmasq,) ## Default: "resolver" # # Defines the name of the DNS forwarder that has to be configured. # Currently implemented are "bind", "dnsmasq" and "resolver", that # causes to write the name server IP addresses to /etc/resolv.conf # only (no forwarder). Empty string defaults to "resolver". # NETCONFIG_DNS_FORWARDER="resolver" ## Type: yesno ## Default: yes # # When enabled (default) in forwarder mode ("bind", "dnsmasq"), # netconfig writes an explicit localhost nameserver address to the # /etc/resolv.conf, followed by the policy resolved name server list # as fallback for the moments, when the local forwarder is stopped. # NETCONFIG_DNS_FORWARDER_FALLBACK="yes" ## Type: string ## Default: "" # # List of DNS domain names used for host-name lookup. # It is written as search list into the /etc/resolv.conf file. # NETCONFIG_DNS_STATIC_SEARCHLIST="" ## Type: string ## Default: "" # # List of DNS nameserver IP addresses to use for host-name lookup. # When the NETCONFIG_DNS_FORWARDER variable is set to "resolver", # the name servers are written directly to /etc/resolv.conf. # Otherwise, the nameserver are written into a forwarder specific # configuration file and the /etc/resolv.conf does not contain any # nameservers causing the glibc to use the name server on the local # machine (the forwarder). See also netconfig(8) manual page. # NETCONFIG_DNS_STATIC_SERVERS="" ## Type: string ## Default: "auto" # # Allows to specify a custom DNS service ranking list, that is which # services provide preferred (e.g. vpn services), and which services # fallback settings (e.g. avahi). # Preferred service names have to be prepended with a "+", fallback # service names with a "-" character. The special default value # "auto" enables the current build-in service ranking list -- see the # netconfig(8) manual page -- "none" or "" disables the ranking. # NETCONFIG_DNS_RANKING="auto" ## Type: string ## Default: "" # # Allows to specify options to use when writting the /etc/resolv.conf, # for example: # "debug attempts:1 timeout:10" # See resolv.conf(5) manual page for details. # NETCONFIG_DNS_RESOLVER_OPTIONS="" ## Type: string ## Default: "" # # Allows to specify a sortlist to use when writting the /etc/resolv.conf, # for example: # 130.155.160.0/255.255.240.0 130.155.0.0" # See resolv.conf(5) manual page for details. # NETCONFIG_DNS_RESOLVER_SORTLIST="" ## Type: string ## Default: "auto" # # Defines the NTP merge policy as documented in netconfig(8) manual page. # Set to "" to disable NTP configuration. # NETCONFIG_NTP_POLICY="auto" ## Type: string ## Default: "" # # List of NTP servers. # NETCONFIG_NTP_STATIC_SERVERS="" ## Type: string ## Default: "auto" # # Defines the NIS merge policy as documented in netconfig(8) manual page. # Set to "" to disable NIS configuration. # NETCONFIG_NIS_POLICY="auto" ## Type: string(yes,no,) ## Default: "yes" # # Defines whether to set the default NIS domain. When enabled and no domain # is provided dynamically or in static settings, /etc/defaultdomain is used. # Valid values are: # - "no" or "" netconfig does not set the domainname # - "yes" netconfig sets the domainname according to the # NIS policy using settings provided by the first # iterface and service that provided it. # - "" as yes, but only using settings from interface. # NETCONFIG_NIS_SETDOMAINNAME="yes" ## Type: string ## Default: "" # # Defines a default NIS domain. # # Further domain can be specified by adding a "_" suffix to # the NETCONFIG_NIS_STATIC_DOMAIN and NETCONFIG_NIS_STATIC_SERVERS # variables, e.g.: NETCONFIG_NIS_STATIC_DOMAIN_1="second". # NETCONFIG_NIS_STATIC_DOMAIN="" ## Type: string ## Default: "" # # Defines a list of NIS servers for the default NIS domain or the # domain specified with same "_" suffix. # NETCONFIG_NIS_STATIC_SERVERS="" ## Type: string ## Default: '' # # Set this variable global variable to the ISO / IEC 3166 alpha2 # country code specifying the wireless regulatory domain to set. # When not empty, ifup-wireless will be set in the wpa_supplicant # config or via 'iw reg set' command. # # Note: This option requires a wpa driver supporting it, like # the 'nl80211' driver used by default since openSUSE 11.3. # When you notice problems with your hardware, please file a # bug report and set e.g. WIRELESS_WPA_DRIVER='wext' (the old # default driver) in the ifcfg file. # See also "/usr/sbin/wpa_supplicant --help" for the list of # available wpa drivers. # WIRELESS_REGULATORY_DOMAIN='' ## Type: integer ## Default: "" # # How log to wait for IPv6 autoconfig in ifup when requested with # the auto6 or +auto6 tag in BOOTPROTO variable. # When unset, a wicked built-in default defer time (10sec) is used. # AUTO6_WAIT_AT_BOOT="" ## Type: list(all,dns,none,"") ## Default: "" # # Whether to update system (DNS) settings from IPv6 RA when requested # with the auto6 or +auto6 tag in BOOTPROTO variable. # Defaults to update if autoconf sysctl (address autoconf) is enabled. # AUTO6_UPDATE="" ## Type: list(auto,yes,no) ## Default: "auto" # # Permits to specify/modify a global ifcfg default. Use with care! # # This settings breaks rules for many things, which require carrier # before they can start, e.g. L2 link protocols, link authentication, # ipv4 duplicate address detection, ipv6 duplicate detection will # happen "post-mortem" and maybe even cause to disable ipv6 at all. # See also "man ifcfg" for further informations. # LINK_REQUIRED="auto" ## Type: string ## Default: "" # # Allows to specify a comma separated list of debug facilities used # by wicked. Negated facility names can be prepended by a "-", e.g.: # "all,-events,-socket,-objectmodel,xpath,xml,dbus" # # When set, wicked debug level is automatically enabled. # For a complete list of facility names, see: "wicked --debug help". # WICKED_DEBUG="" ## Type: list("",error,warning,notice,info,debug,debug1,debug2,debug3) ## Default: "" # # Allows to specify wicked debug level. Default level is "notice". # WICKED_LOG_LEVEL=""
examples:
/etc/sysconfig/network/ifcfg- <configuration-name>
The files containing the configuration of the devices. An example that shows a typical configuration with the name ifcfg-eth0:
IPADDRESS=10.10.11.184
NETMASK=255.255.0.0
BROADCAST=10.10.255.255
STARTMODE=onboot
BOOTPROTO=static
/etc/sysconfig/network/ifroute- <configuration-name>
You can specify individual routes for every configuration in these files. See routes (5) for a detailed description.
liked this article?
- only together we can create a truly free world
- plz support dwaves to keep it up & running!
- (yes the info on the internet is (mostly) free but beer is still not free (still have to work on that))
- really really hate advertisement
- contribute: whenever a solution was found, blog about it for others to find!
- talk about, recommend & link to this blog and articles
- thanks to all who contribute!