Debian 12
as systemd is installed per default but not the time-sync service #wtf?
su - root apt install systemd-timesyncd timedatectl set-timezone Europe/Berlin systemctl status systemd-timesyncd timedatectl; # check if sync is on Local time: Fri 2023-12-08 16:21:41 CET Universal time: Fri 2023-12-08 15:21:41 UTC RTC time: Fri 2023-12-08 15:21:41 Time zone: Europe/Berlin (CET, +0100) System clock synchronized: yes <- it works NTP service: active RTC in local TZ: no
systemd: So WHAT NTP time server does systemd use per default?
no one knows.
https://manpages.debian.org/bullseye/systemd/systemd-system.conf.5.en.html “The default configuration is defined during compilation, so a configuration file is only needed when it is necessary to deviate from those defaults. By default, the configuration file in /etc/systemd/ contains commented out entries showing the defaults as a guide to the administrator. This file can be edited to create local overrides.”
so NTP servers of sytemd are somewhat “hardcoded” on buildtime, which is VERY strange behavior as any good service would surely write read config files per default and MAYBE use the local Fritzbox NTP server 192.168.0.1 per default but no.
According to wireshark systemd-timesyncd is sugin this server: no idea who is running those servers https://www.ntppool.org/it/scores/178.63.52.50 https://www.whois.com/whois/178.63.52.50
No. Time Source Destination Protocol Length Info 12 4.774228252 192.168.0.XX 178.63.52.50 NTP 90 NTP Version 4, client 13 4.811397099 178.63.52.50 192.168.0.XX NTP 90 NTP Version 4, server Destination Address: 178.63.52.50 User Datagram Protocol, Src Port: 52165, Dst Port: 123 Source Port: 52165 Destination Port: 123 Length: 56 Checksum: 0x92c3 [unverified] UDP payload (48 bytes) Network Time Protocol (NTP Version 4, client)
specify ntp server to use:
su - root cp -rv /etc/systemd/timesyncd.conf /etc/systemd/timesyncd.conf.backup echo ' [Time] NTP=192.168.0.1 FallbackNTP=0.debian.pool.ntp.org 1.debian.pool.ntp.org 2.debian.pool.ntp.org 3.debian.pool.ntp.org ' >> /etc/systemd/timesyncd.conf systemctl restart systemd-timesyncd
file access modify creation time will always be in UTC format.
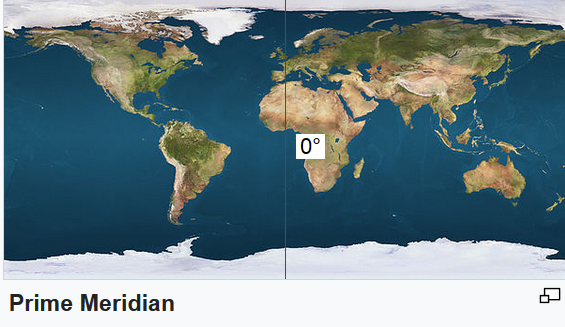
In which time offset is +hours or -hours from Longitude: 0° (Prime Meridian)
Prime meridian (Greenbich) GPS: 0° 00′ 05.3101″ W
Other names: Z / Zulu Time Zone
Time Zone: UTC
date -u; # output UTC time
At sea: Longitudes between 7.5° West and 7.5° East

US-President Obama in the National Counterterrorism Center in McLean in 2015. In the top left corner you can see Zulu-time.
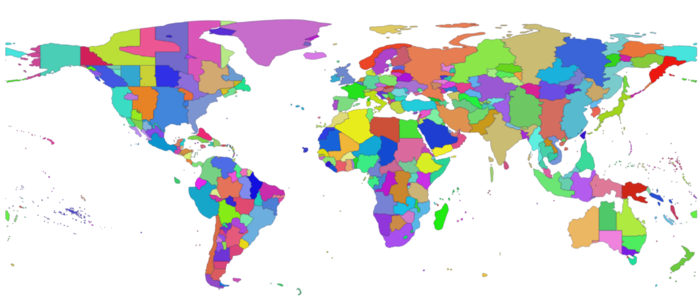
World map showing time zones from the tz database version 2017a – src: https://github.com/evansiroky/timezone-boundary-builder “A tool to extract data from Open Street Map (OSM) to build the boundaries of the world’s timezones that includes territorial waters.”
Author Evan Siroky
changing timezones
you could set
timedatectl list-timezones; # list all available timezones: (works Centos7, Debian8, Suse12) suse12:~ # timedatectl; # print currently used timezone Local time: Wed 2017-06-07 11:32:35 CEST Universal time: Wed 2017-06-07 09:32:35 UTC RTC time: Tue 2017-06-06 18:33:12 Time zone: Europe/Berlin (CEST, +0200) Network time on: no NTP synchronized: no RTC in local TZ: no # permanently change timezone to America/Chicago (works Centos7, Debian8, Suse12) timedatectl set-timezone America/Chicago # alternatively interactive mode tzselect # debian only alternative: dpkg-reconfigure tzdata
changing time zones manually
the file /etc/localtime contains the currently used timezone.
on debian this file is an copy of a file from /usr/share/zoneinfo/
on most distroy this is a softlink to a file below /usr/share/zoneinfo/
unfortunately hwlock can not work with softlinks?
root@Debian8:~# file /etc/localtime /etc/localtime: timezone data, version 2, 8 gmt time flags, 8 std time flags, no leap seconds, 144 transition times, 8 abbreviation chars [root@CentOS7 ~]# file /etc/localtime /etc/localtime: symbolic link to `../usr/share/zoneinfo/Europe/Berlin' suse12:~ # file /etc/localtime /etc/localtime: symbolic link to `../usr/share/zoneinfo/Europe/Berlin' # so to manually change your timezone to "Chicago" you would unlink /etc/localtime; ln -sv /usr/share/zoneinfo/America/Chicago /etc/localtime;
per user time-zone settings
you could specify a different time-zone for every user via the TZ environment variable
# in user's .bashrc you would put
export TZ=:/usr/share/zoneinfo/America/Dominica
network time
also checkout systemd time sync
the time of your server/pc can be synced with time-servers that read time from an attached atomic-clock.
having wrong date and time set may result in all sorts of errors – including browsers not accepting SSL certificates. (because they are not YET valid or have expired)
timedatectl; # will tell you if your clock was synced with an time server and if ntp service is working root@debian8:~# apt get install ntp; # ntp service needs to be installed first root@CentOS7 user]# yum install ntp; # ntp service needs to be installed first ntpd -q -g; # sync local time with timeserver - works on debian8 and centos7 ntpd: time slew +0.005187s # sync system-time to cmos-hardware-realtime-clock (BIOS) hwclock --systohc; # edit network time protocol config vim /etc/ntp.conf # add those if you are in Germany (de) # if you are in China use (cn) # check out: http://www.pool.ntp.org/en/ for more servers # you may change those time servers to what you think works best
server 0.de.pool.ntp.org server 1.de.pool.ntp.org server 2.de.pool.ntp.org server 3.de.pool.ntp.org ESC :wq # vim save and quit # debian8 service ntp restart; # centos7, suse12, newer debian9? systemctl restart ntpd.service; # query the service ntpdc -c sysinfo; system peer: stratum2-4.ntp.techfak.net system peer mode: client leap indicator: 00 stratum: 3 precision: -21 root distance: 0.03188 s root dispersion: 0.02847 s reference ID: [129.70.132.37] reference time: dce92737.5c99f8b6 Mon, Jun 12 2017 16:44:07.361 system flags: auth monitor ntp kernel stats jitter: 0.001678 s stability: 0.000 ppm broadcastdelay: 0.000000 s authdelay: 0.000000 s suse12:# rcntpd addserver de.pool.ntp.org; # add server as time-server suse12:# ntpd -q -g; # takes very long... kind of stuck somewhere? 7 Jun 11:50:09 ntpd[2153]: ntpd 4.2.8p8@1.3265-o Mon Jun 6 08:13:03 UTC 2016 (1): Starting 7 Jun 11:50:09 ntpd[2153]: Command line: ntpd -q -g 7 Jun 11:50:09 ntpd[2153]: proto: precision = 0.200 usec (-22) authreadkeys: full access list <NULL> 7 Jun 11:50:09 ntpd[2153]: switching logging to file /var/log/ntp 7 Jun 11:50:09 ntpd[2153]: Listen and drop on 0 v6wildcard [::]:123 7 Jun 11:50:09 ntpd[2153]: Listen and drop on 1 v4wildcard 0.0.0.0:123 7 Jun 11:50:09 ntpd[2153]: Listen normally on 2 lo 127.0.0.1:123 7 Jun 11:50:09 ntpd[2153]: Listen normally on 3 eth0 172.20.0.25:123 7 Jun 11:50:09 ntpd[2153]: Listen normally on 4 lo [::1]:123 7 Jun 11:50:09 ntpd[2153]: Listen normally on 5 eth0 [fe80::215:5dff:fe00:709%2]:123 7 Jun 11:50:09 ntpd[2153]: Listening on routing socket on fd #22 for interface updates
/etc/timezone
root@debian8:~# cat /etc/timezone Europe/Berlin root@Debian8:~# date Wed Jun 7 10:30:48 CEST (Central European Summer Time) 2017 suse12:# cat /etc/sysconfig/clock; # this seems to be a SUSE only file, neither Debian8 nor Centos7 have it TIMEZONE="Europe/Berlin" DEFAULT_TIMEZONE="US/Eastern"
timezone info files
seems to be binary files of some sort that define a timezone
root@Debian8:~# file /usr/share/zoneinfo/America/Dominica /usr/share/zoneinfo/America/Dominica: symbolic link to Marigot root@Debian8:~# file /usr/share/zoneinfo/America/Marigot /usr/share/zoneinfo/America/Marigot: timezone data, version 2, 2 gmt time flags, 2 std time flags, no leap seconds, 1 transition time, 2 abbreviation chars suse12:~ # file /usr/share/zoneinfo/America/Dominica /usr/share/zoneinfo/America/Dominica: timezone data, version 2, 2 gmt time flags, 2 std time flags, no leap seconds, 2 transition times, 2 abbreviation chars [root@CentOS7 ~]# file /usr/share/zoneinfo/America/Dominica /usr/share/zoneinfo/America/Dominica: timezone data, version 2, 2 gmt time flags, 2 std time flags, no leap seconds, 1 transition time, 2 abbreviation chars
temporary timezone changes
works on Debian8 and CentOS7 as well.
suse12:# export TZ=:/usr/share/zoneinfo/America/Dominica suse12:# date Mi 7. Jun 04:34:22 AST (Atlantic Standard Time) 2017
locale
locale basically defines country-wise-settings in terms of charset, currency and formatting (e.g. 1,000,00 USD vs 1000€)
locale -a; # show all available (installed) locale-definition files (does not display all locales in Debian8?) locale -m; # display all available charsets dpkg-reconfigure locales; # Debian8 only - change locale
this way you can change language of the entire system:
example output: locale_m_debian8_available_charsets.txt
root@Debian8:~# locale -a| grep en_US en_US.utf8 [root@CentOS7 ~]# locale -a| grep en_US en_US en_US.iso88591 en_US.iso885915 en_US.utf8 suse12:~ # locale -a| grep en_US en_US en_US.iso885915 en_US.utf8
the files are located under:
root@Debian8:~# /usr/share/i18n/locales/ [root@CentOS7 ~]# /usr/share/i18n/locales/ [root@CentOS7 ~]# file /usr/share/i18n/locales/wo_SN /usr/share/i18n/locales/wo_SN: ISO-8859 text
wo_SN.txt (source “The Debian Project” -> so Suse12 and CentOS use some Debian files 😉
suse12:~ # /usr/share/i18n/locales/ root@Debian8:~# locale LANG=en_US.UTF-8 LANGUAGE=en_US:en LC_CTYPE="en_US.UTF-8" LC_NUMERIC="en_US.UTF-8" LC_TIME="en_US.UTF-8" LC_COLLATE="en_US.UTF-8" LC_MONETARY="en_US.UTF-8" LC_MESSAGES="en_US.UTF-8" LC_PAPER="en_US.UTF-8" LC_NAME="en_US.UTF-8" LC_ADDRESS="en_US.UTF-8" LC_TELEPHONE="en_US.UTF-8" LC_MEASUREMENT="en_US.UTF-8" LC_IDENTIFICATION="en_US.UTF-8" LC_ALL= suse12:~ # locale LANG=de_DE.UTF-8 LC_CTYPE="de_DE.UTF-8" LC_NUMERIC="de_DE.UTF-8" LC_TIME="de_DE.UTF-8" LC_COLLATE="de_DE.UTF-8" LC_MONETARY="de_DE.UTF-8" LC_MESSAGES="de_DE.UTF-8" LC_PAPER="de_DE.UTF-8" LC_NAME="de_DE.UTF-8" LC_ADDRESS="de_DE.UTF-8" LC_TELEPHONE="de_DE.UTF-8" LC_MEASUREMENT="de_DE.UTF-8" LC_IDENTIFICATION="de_DE.UTF-8" LC_ALL= [root@CentOS7 ~]# locale LANG=de_DE.UTF-8 LC_CTYPE="de_DE.UTF-8" LC_NUMERIC="de_DE.UTF-8" LC_TIME="de_DE.UTF-8" LC_COLLATE="de_DE.UTF-8" LC_MONETARY="de_DE.UTF-8" LC_MESSAGES="de_DE.UTF-8" LC_PAPER="de_DE.UTF-8" LC_NAME="de_DE.UTF-8" LC_ADDRESS="de_DE.UTF-8" LC_TELEPHONE="de_DE.UTF-8" LC_MEASUREMENT="de_DE.UTF-8" LC_IDENTIFICATION="de_DE.UTF-8" LC_ALL=
lang
there are environment variables that define the currently used language.
“$LC_ALL environment variable will overrides all other ($LC_LANG, $LANG) localisation settings (except $LANGUAGE under some circumstances)”. (src)
currently used OS set-language. can also affect sorting of directories.
root@Debian8:~# echo $LANG en_US.UTF-8 [root@CentOS7 ~]# echo $LANG de_DE.UTF-8 suse12:~ # echo $LANG de_DE.UTF-8 suse12:/home/user/test # export LANG=de_DE.UTF-8 suse12:/home/user/test # ll insgesamt 0 -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 7. Jun 11:10 apple -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 7. Jun 11:10 Apple -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 7. Jun 11:10 banana -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 7. Jun 11:10 Banana suse12:/home/user/test # export LANG=POSIX suse12:/home/user/test # ll total 0 -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Jun 7 11:10 Apple -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Jun 7 11:10 Banana -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Jun 7 11:10 apple -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Jun 7 11:10 banana
manpages
“It comes handy when you want to know what time it is in other countries, or if you just wonder what timezones exist.”
Links:
https://dwaves.de/2017/06/20/linux-debian8-change-language-of-entire-system/
https://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/centos-linux-6-7-changing-timezone-command-line/
http://www.leapsecond.com/java/gpsclock.htm
https://www.timeanddate.com/worldclock/timezone/zulu
RFCs:
ntp protocol – https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc1305
liked this article?
- only together we can create a truly free world
- plz support dwaves to keep it up & running!
- (yes the info on the internet is (mostly) free but beer is still not free (still have to work on that))
- really really hate advertisement
- contribute: whenever a solution was found, blog about it for others to find!
- talk about, recommend & link to this blog and articles
- thanks to all who contribute!